Calling Cardano-Rust from Android App
Following on from the previous post about calling Cardano-Rust code from C…..
We are going to call the same Rust functions from an Android app.
Source code discussed below is here, but with binaries and local config omitted.
Android allows you to call C library functions from Java using JNI. We have already taken care of the Rust-to-C part, by making the special bridging functions, as seen in the previous post. We now need to do the Java-to-C part and make an app.
We will use Android Studio to make the app that calls the Rust functions. Several bits and pieces are required, which are installable from within studio: NDK, Cmake, LLDB. The NDK (native development kit) contains compilers for the different Android hardware platforms, when installing, note the location. You will also see it later specified in the local.properties file under “Gradle Scripts” once you make a project.
The Rust Side
In the previous post we compiled the Rust library for the local machine because the code would run on the local machine, however in this case the code should be compiled on the local machine for Android hardware, a “cross compilation”. We need to build a version of the library for the various Android hardware platforms. We can use either a static (.a) or dynamic (.so) linked library, we will use a statically linked library.
Check that Cargo.toml specifies static crate type under the [lib] section:
crate-type = ["staticlib"]
We will build for 4 hardware platforms, that will cover 99% of Android phones. We need to download bits for each:
rustup target add aarch64-linux-android
rustup target add armv7-linux-androideabi
rustup target add i686-linux-android
rustup target add x86_64-linux-android
We specify the relevant NDK archiver and linker for each target in .cargo/config file, this will vary depending on the location:
[target.aarch64-linux-android]
ar = "/Users/NDK/arm64/bin/aarch64-linux-android-ar"
linker = "/Users//NDK/arm64/bin/aarch64-linux-android-clang"
[target.armv7-linux-androideabi]
ar = "/Users//NDK/arm/bin/arm-linux-androideabi-ar"
linker = "/Users/NDK/arm/bin/arm-linux-androideabi-clang"
[target.i686-linux-android]
ar = "/Users/NDK/x86/bin/i686-linux-android-ar"
linker = "/Users/NDK/x86/bin/i686-linux-android-clang"
[target.x86_64-linux-android]
ar = "/Users/NDK/x86/bin/i686-linux-android-ar"
linker = "/Users/NDK/x86/bin/i686-linux-android-clang"
Then build for each platform:
cargo build --target aarch64-linux-android
cargo build --target armv7-linux-androideabi
cargo build --target i686-linux-android
cargo build --target x86_64-linux-android
NB: can add –release to create optimised code, else it will make debug version, for this demo it doesn’t matter.
As before we find the .a somewhere under target/ and check it has the functions:
pusheen: nm ./target/aarch64-linux-android/debug/libtest.a | grep my_b58_
0000000000000000 T my_b58_decode
0000000000000000 T my_b58_encode
I create a new minimal project called android_b58.
We need to add our libraries to the Android project. Under src/main, we create jniLibs directory with subdirectories corresponding to the three Android platforms; arm64-v8a, armeabi-v7a, x86_64. We can copy and rename each libtest.so (or whatever they are called) to libcardano_funcs.so (or anything descriptive). For me it looked like this:
cp ./aarch64-linux-android/debug/libtest.a /android_b58/src/main/jniLibs/arm64-v8a/libcardano_funcs.a
cp ./armv7-linux-androideabi/debug/libtest.a /android_b58/src/main/jniLibs/armeabi-v7a/libcardano_funcs.a
cp ./i686-linux-android/debug/libtest.a /android_b58/src/main/jniLibs/x86/libcardano_funcs.a
cp ./x86_64-linux-android/debug/libtest.a /android_b58/src/main/jniLibs/x86_64/libcardano_funcs.a
Under jniLibs, we make “include” folder, with the header file called cardano_funcs.h containing the C function declarations:
int8_t my_b58_encode( const uint8_t *bytes, unsigned int size, char *encoded );
int8_t my_b58_decode( const char *encoded, uint8_t *bytes );
The Android Side
To call our two library functions from Java, we create another library, linked with the libcardano_funcs library. This new library is the interface, it very thin and simple, it makes the functions callable from Java, it uses JNI. It is written in C, and is a simple wrapper for each function we want to call, it will be built automatically using the gradle build system.
Under /src/main we make a “c” directory, which contains load-lib.c containing the simple function wrappers which will be linked with libcardano_funcs.so to make load-lib library which we will use in this app. We will also make a file CmakeLists.txt containing the instructions for cmake to build the library.
The file load-lib.c which calls our functions using JNI interface:
#include <jni.h>
#include <android/log.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <cardano_funcs.h>
// Macro: allocate memory for number of type and set memory to NULL
#define ZERO(ptr,bytes) memset( (void *)ptr, '\0', bytes )
#define MEMORY(number,type) ZERO( malloc( sizeof(type) * number ), sizeof(type) * number )
#define LOGI(...) \
((void)__android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_INFO, "load-libs::", __VA_ARGS__))
JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL Java_test_cardano_MainActivity_encodeBase58(JNIEnv *env, jobject thiz, jbyteArray javaByteArray) {
clock_t start_t, end_t;
double cpu_time_used;
start_t = clock();
jbyte *bytePtr = (*env)->GetByteArrayElements(env, javaByteArray, NULL);
jint bytePtrSize = (*env)->GetArrayLength(env, javaByteArray);
char *encoded = (char *)MEMORY(1000,char); // TODO: required size = ceil(log(256^a, 58))
// call library function
int status = my_b58_encode( (uint8_t *)bytePtr, (int)bytePtrSize, encoded );
jstring jEncodedString;
char *log_msg = (char *)MEMORY(1000,char);
if ( status <0 ) {
jEncodedString = NULL;
sprintf(log_msg,"There was an error");
} else {
jEncodedString = (*env)->NewStringUTF(env, encoded);
sprintf(log_msg,"in (%s), out (%s)",encoded,(char *)bytePtr);
}
free(encoded);
(*env)->ReleaseByteArrayElements(env, javaByteArray, bytePtr, 0);
end_t = clock();
cpu_time_used = (double)(end_t - start_t) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
LOGI("encodeBase58 calculation time: %f, %s \n", cpu_time_used, log_msg);
free(log_msg);
return jEncodedString;
}
JNIEXPORT jbyteArray JNICALL Java_test_cardano_MainActivity_decodeBase58(JNIEnv *env, jobject thiz, jstring javaEncodedString) {
clock_t start_t, end_t;
double cpu_time_used;
start_t = clock();
const char *encoded = (*env)->GetStringUTFChars(env, javaEncodedString, 0);
uint8_t *bytePtr = (uint8_t *)MEMORY(1000,uint8_t); // TODO: sized
// call library function
int status = my_b58_decode( encoded, bytePtr );
jbyteArray jDecodedBytes = NULL;
char *log_msg = (char *)MEMORY(1000,char);
if ( status <0 ) {
jDecodedBytes = NULL;
sprintf(log_msg,"There was an error");
} else {
jDecodedBytes = (*env)->NewByteArray(env, strlen((char*)bytePtr));
(*env)->SetByteArrayRegion(env,jDecodedBytes,0,strlen((char*)bytePtr),bytePtr);
sprintf(log_msg,"in (%s), out (%s)",encoded,(char *)bytePtr);
}
free(bytePtr);
(*env)->ReleaseStringUTFChars(env, javaEncodedString, encoded);
end_t = clock();
cpu_time_used = (double)(end_t - start_t) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
LOGI("decodeBase58 calculation time: %f, %s \n", cpu_time_used,log_msg);
return jDecodedBytes;
}
The file CmakeLists.txt which instructs gradle on building the library:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.4.1)
set(distribution_DIR ${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/../jniLibs)
add_library(lib_cardano_funcs STATIC IMPORTED)
set_target_properties(lib_cardano_funcs PROPERTIES IMPORTED_LOCATION
${distribution_DIR}/${ANDROID_ABI}/libcardano_funcs.a)
# build application's shared lib
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -std=gnu++11")
add_library(load-libs SHARED
load-libs.c)
target_include_directories(load-libs PRIVATE
${distribution_DIR}/include)
target_link_libraries(load-libs
android
lib_cardano_funcs
log)
We modify build.gradle so that these actions are done automatically. In root/android/defaultConfig section add:
ndk {
abiFilters 'armeabi-v7a', 'arm64-v8a', 'x86', 'x86_64'
}
externalNativeBuild {
cmake {
arguments '-DANDROID_STL=c++_static'
}
}
And within root/android part of the same file add:
externalNativeBuild {
cmake {
path 'src/main/c/CMakeLists.txt'
}
}
At this point we can do a build in Android Studio, it should all work. You will see the libload-lib.so in build/intermediaries, and in the apk:
pusheen: unzip -l outputs/apk/debug/android_b58-debug.apk | grep libload-libs.so
5952 00-00-1980 00:00 lib/arm64-v8a/libload-libs.so
9836 00-00-1980 00:00 lib/armeabi-v7a/libload-libs.so
5684 00-00-1980 00:00 lib/x86/libload-libs.so
6288 00-00-1980 00:00 lib/x86_64/libload-libs.so
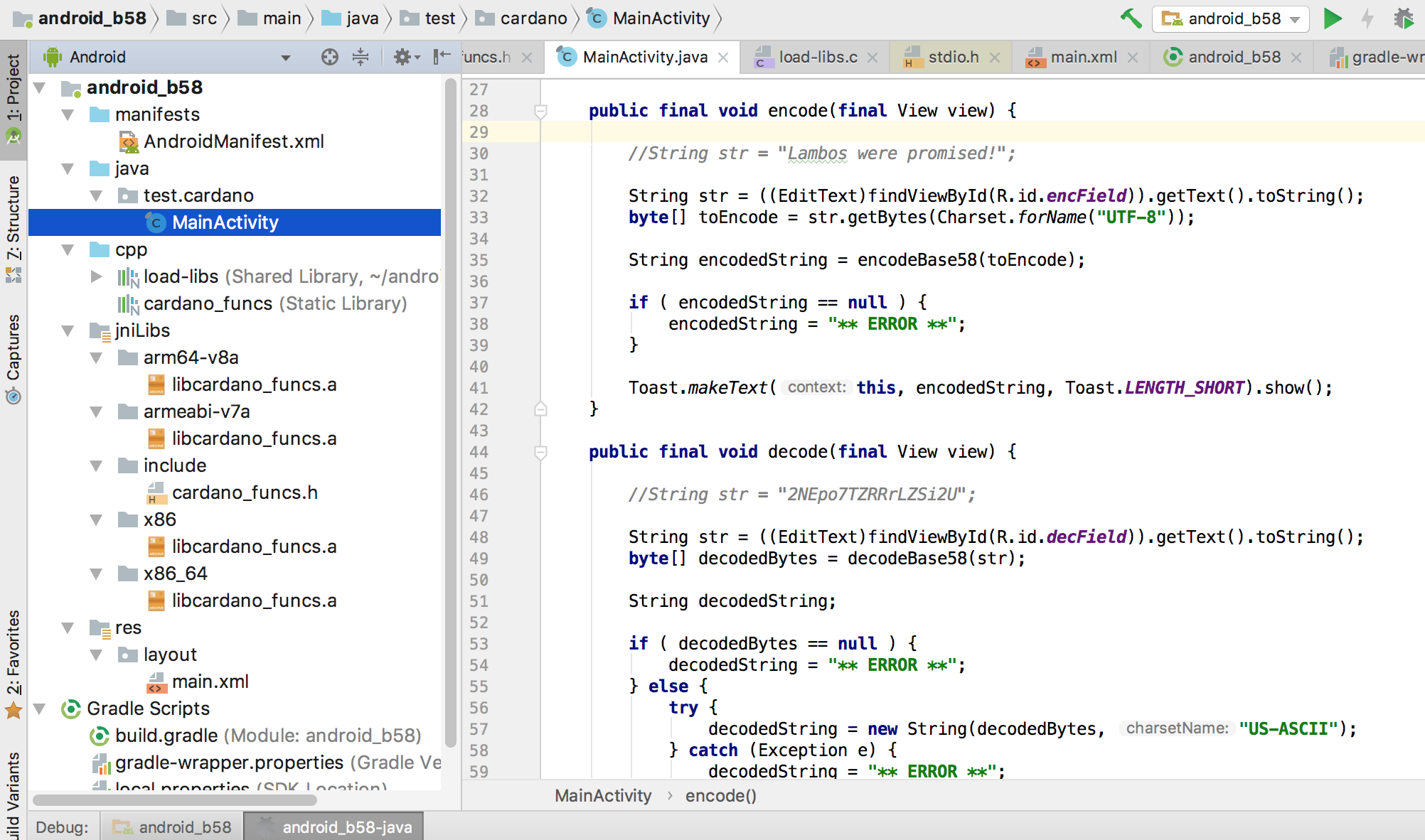
Here is a screenshot of the project:
We want to call our functions from the app. We declare the native functions and load the library in Java using this statement with the undecorated library name in MainActivity:
public native String encodeBase58(byte[] byteArrayToEncode);
public native byte[] decodeBase58(String b58StringToDecode);
static {
System.loadLibrary("load-libs");
}
We make a simple GUI with two EditText fields and two corresponding buttons, encode and decode. The event functions for the buttons are as follows:
public final void encode(final View view) {
String str = ((EditText)findViewById(R.id.encField)).getText().toString();
byte[] toEncode = str.getBytes(Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
String encodedString = encodeBase58(toEncode);
if ( encodedString == null ) {
encodedString = "** ERROR **";
}
Toast.makeText(this, encodedString, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
public final void decode(final View view) {
String str = ((EditText)findViewById(R.id.decField)).getText().toString();
byte[] decodedBytes = decodeBase58(str);
String decodedString;
if ( decodedBytes == null ) {
decodedString = "** ERROR **";
} else {
try {
decodedString = new String(decodedBytes, "US-ASCII");
} catch (Exception e) {
decodedString = "** ERROR **";
}
}
Toast.makeText(this, decodedString, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
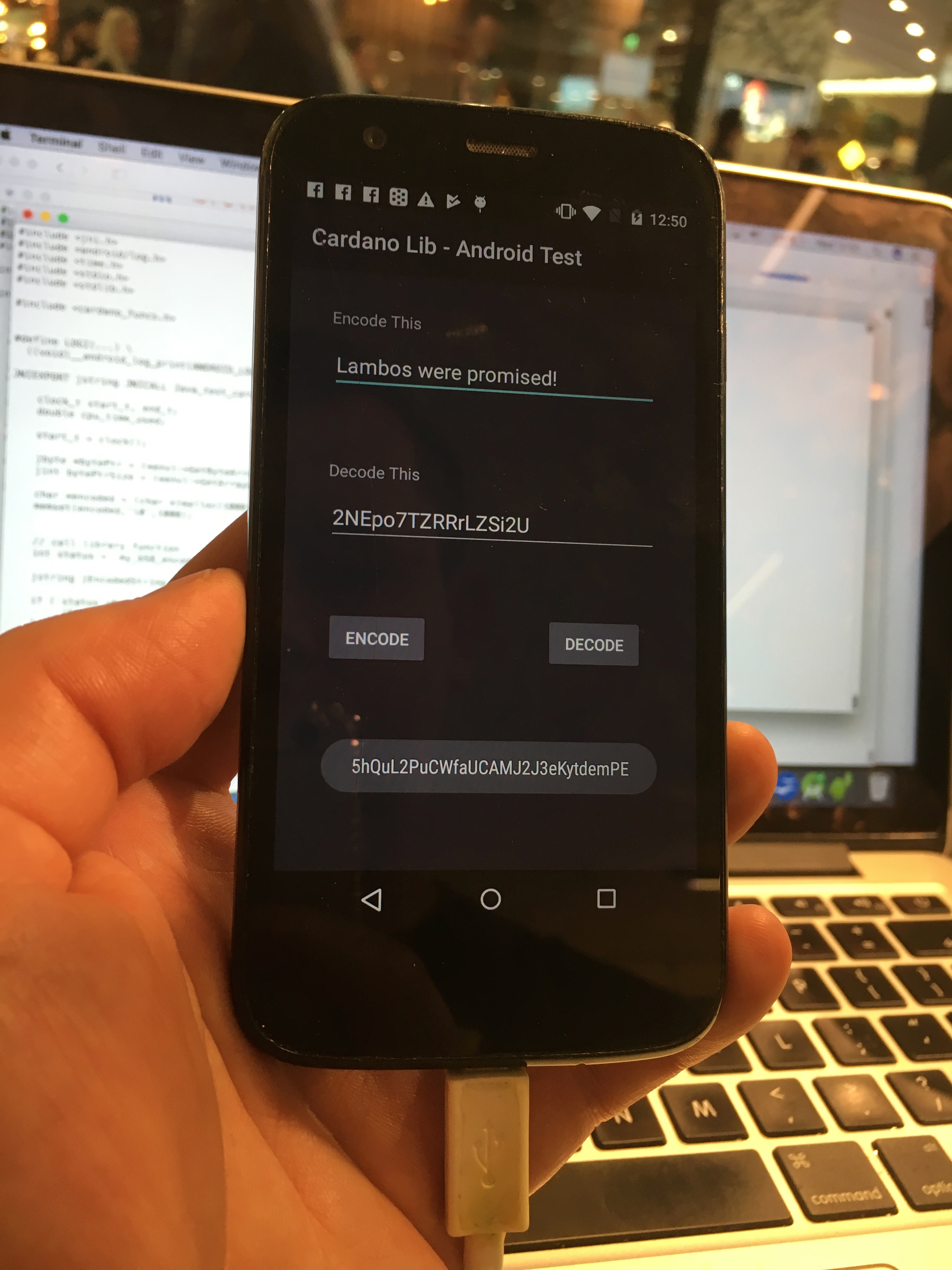
That’s about it. We run the app on a mobile, type something into the encode field, tap encode button – pops up the base58 text. Or type in base58 text, tap decode and it pops up the plain text.
Code is here, but with binaries and local config omitted.